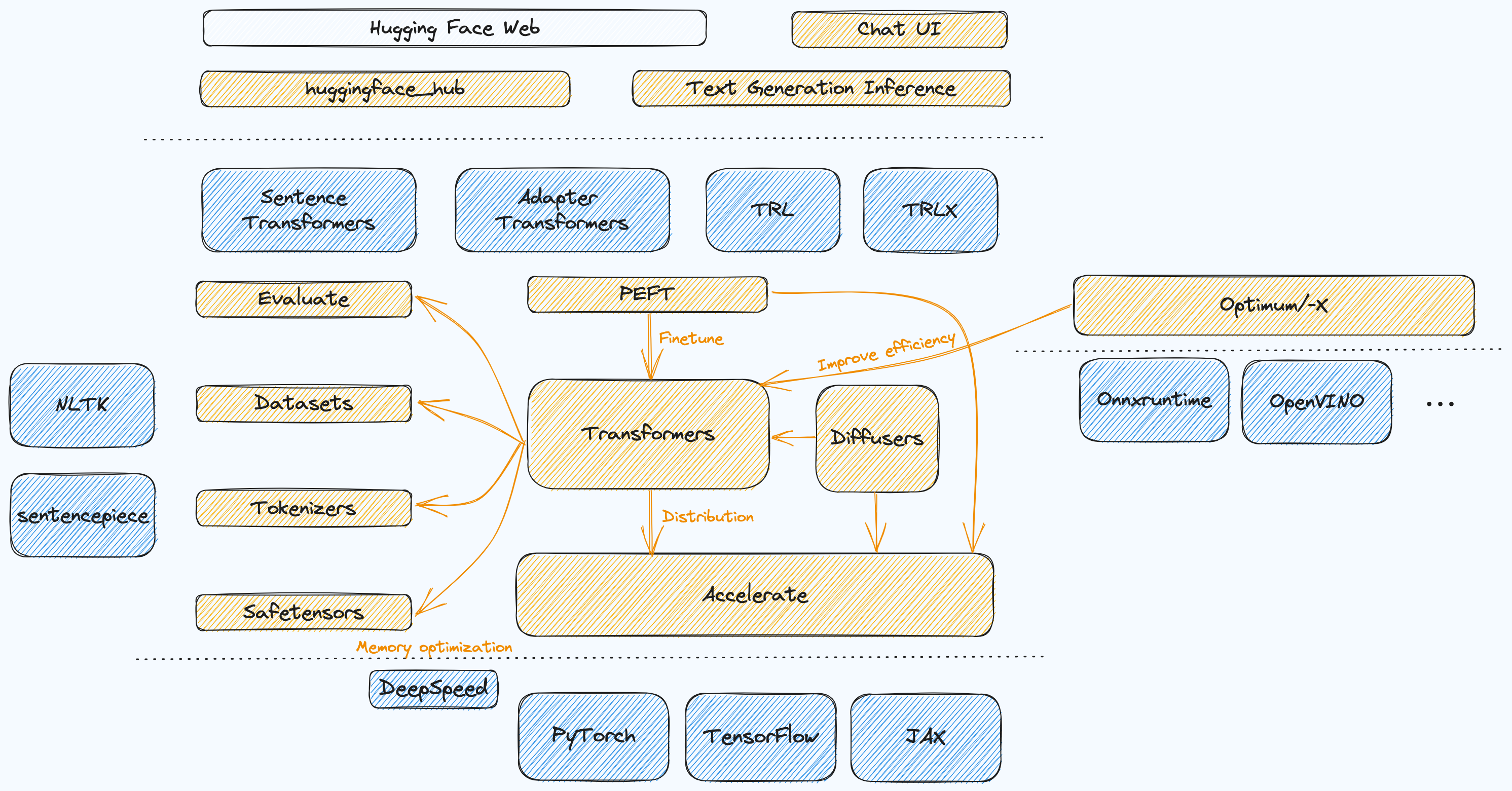
Hugging Face 主要项目全景图
Hugging Face 提供了一整套 LLM 开发工具链,从数据集构建、模型开发管理、到应用构建都有相关项目进行支持,而且还与自家官网提供的数据/模型仓库、应用部署服务无缝对接。下图简单整理了 Hugging Face 主要仓之间的关系,黄色是 Hugging Face 自家项目,蓝色是其它三方项目
大致依赖关系从左到右,从下到上,Transformers 作为核心库提供模型结构定义以及运行方法,Accelerate 提供分布式训练能力,PEFT 用来做模型高效微调,Optimum 主要针对特定硬件做性能优化,左边一列主要是数据集、评价指标、分词等辅助库,上层通过 huggingface_hub 与远端仓库进行模型/数据的上传和下载,Text Generation Inference 可以实现模型的部署,通过 RestFul API 进行调用,最上层还提供了 Chat UI 来构建 Web 应用
除了自家项目,也有不少高质量的外部项目集成了 Hugging Face 或被 Hugging Face 依赖,例如最底层的 AI 框架 PyTorch, TensorFLow, JAX,内存优化库 DeepSpeed,Runtime 执行加速库 Onnxruntime, OpenVINO,分词工具 NLTK, sentencepiece,强化学习 RLHF 库 TRL 和 TRLX,还有专门通过 LoRA 等技术在不改变模型权重的条件下,做轻量化适配层的 Adapter Transformers 等
主要项目介绍
1. Transformers
- 提供上千种预训练模型,可用于文本、图像、音频领域
- 提供模型下载与上传接口,提供训练接口
- 支持三种后端
PyTorch,TensorFlow和JAX
模型下载与使用样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, GPT2Model
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
model = GPT2Model.from_pretrained("gpt2")
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute", return_tensors="pt")
outputs = model(**inputs)
last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
模型训练样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer, logging
logging.set_verbosity_error()
training_args = TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=4, **default_args)
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
result = trainer.train()
print_summary(result)
模型上传样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 用法1: 训练后上传
training_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="my-awesome-model", push_to_hub=True)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=small_train_dataset,
eval_dataset=small_eval_dataset,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
)
trainer.push_to_hub()
# 用法2: 直接上传
pt_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
2. Accelerate
- 分布式训练库,支持
DeepSpeed后端进行显存优化 - 在不改变原有
PyTorch代码逻辑基础上,仅需添加几行代码 - 支持多种硬件的单机/多机训练
训练代码与 PyTorch 对比样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from datasets import load_dataset
+ from accelerate import Accelerator
- device = 'cpu'
+ accelerator = Accelerator()
- model = torch.nn.Transformer().to(device)
+ model = torch.nn.Transformer()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
dataset = load_dataset('my_dataset')
data = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, shuffle=True)
+ model, optimizer, data = accelerator.prepare(model, optimizer, data)
model.train()
for epoch in range(10):
for source, targets in data:
- source = source.to(device)
- targets = targets.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(source)
loss = F.cross_entropy(output, targets)
- loss.backward()
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
optimizer.step()
3. PEFT
- 高效大模型微调库,微调局部参数,以降低计算和存储成本
- 支持 LoRA, Prefix Tuning, P-Tuning 等5种主流微调方法
利用 PEFT 构建训练参数样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType
model_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
tokenizer_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
peft_config = LoraConfig(
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
)
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
model.print_trainable_parameters()
# output: trainable params: 2359296 || all params: 1231940608 || trainable%: 0.19151053100118282
通过训练参数占比可以看出,该库为在消费级 GPU 卡上微调模型提供可能
Hardware: Single A100 80GB GPU with CPU RAM above 64GB | Model | Full Finetuning | PEFT-LoRA PyTorch | PEFT-LoRA DeepSpeed with CPU Offloading | | —- | —- | —- | —- | | bigscience/T0_3B (3B params) | 47.14GB GPU / 2.96GB CPU | 14.4GB GPU / 2.96GB CPU | 9.8GB GPU / 17.8GB CPU | | bigscience/mt0-xxl (12B params) | OOM GPU | 56GB GPU / 3GB CPU | 22GB GPU / 52GB CPU | | bigscience/bloomz-7b1 (7B params) | OOM GPU | 32GB GPU / 3.8GB CPU | 18.1GB GPU / 35GB CPU |
4. Optimum
Transformers和Diffuser训练推理优化工具,可以最大限度地提高在目标硬件上训练和运行模型的效率,同时保持易用性- Optimum 仓库原生支持后端如下表所示,其它硬件设备的适配可以另外构建
Optimum-X仓库,例如optimum-habana针对 HPU 硬件进行加速
原生支持后端
| Accelerator | Installation |
|---|---|
| ONNX Runtime | python -m pip install optimum[onnxruntime] |
| Intel Neural Compressor | python -m pip install optimum[neural-compressor] |
| IOpenVINO | python -m pip install optimum[openvino,nncf] |
| Habana Gaudi Processor (HPU) | python -m pip install optimum[habana] |
后端支持特性对比
| Features | ONNX Runtime | Neural Compressor | OpenVINO | TensorFlow Lite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graph optimization | ✔️ | N/A | ✔️ | N/A |
| Post-training dynamic quantization | ✔️ | ✔️ | N/A | ✔️ |
| Post-training static quantization | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Quantization Aware Training (QAT) | N/A | ✔️ | ✔️ | N/A |
| FP16 (half precision) | ✔️ | N/A | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Pruning | N/A | ✔️ | ✔️ | N/A |
| Knowledge Distillation | N/A | ✔️ | ✔️ | N/A |
OpenVINO 后端样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
+ from optimum.intel import OVModelForSequenceClassification
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, pipeline
model_id = "distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
- model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_id)
+ model = OVModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_id, export=True)
model.save_pretrained("./distilbert")
classifier = pipeline("text-classification", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
results = classifier("He's a dreadful magician.")
ONNX Runtime 后端样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
- from transformers import AutoModelForQuestionAnswering
+ from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTModelForQuestionAnswering
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, pipeline
model_id = "deepset/roberta-base-squad2"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
- model = AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained(model_id)
+ model = ORTModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("roberta_base_qa_onnx")
qa_pipe = pipeline("question-answering", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
question = "What's Optimum?"
context = "Optimum is an awesome library everyone should use!"
results = qa_pipe(question=question, context=context)
5. Datasets
- 公开数据集下载和上传,构建 data_loader 数据加载器
- 高效的数据预处理,对 CSV、JSON、text、PNG、JPEG、WAV、MP3、Parquet 等本地数据集进行简单、快速和可复制的数据预处理器
- 创建自定义数据集
数据集下载样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
from datasets import load_dataset
# 一次性下载
dataset = load_dataset("rotten_tomatoes", split="train")
# 每次取一个样本
iterable_dataset = load_dataset("food101", split="train", streaming=True)
for example in iterable_dataset:
print(example)
# 取前3个样本
list(iterable_dataset.take(3))
图片预处理样例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
def transforms(examples):
examples["pixel_values"] = [image.convert("RGB").resize((100,100)) for image in examples["image"]]
return examples
# 用法1
dataset = dataset.map(transforms, remove_columns=["image"], batched=True)
# 方法2
dataset.set_transform(transforms)
6. Tokenizers
- 支持分词器训练
- 实现快速分词
加载与训练分词器样例
1
2
3
from tokenizers import Tokenizer
tokenizer = Tokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
训练分词器样例
1
2
3
4
from tokenizers.trainers import BpeTrainer
trainer = BpeTrainer(special_tokens=["[UNK]", "[CLS]", "[SEP]", "[PAD]", "[MASK]"])
tokenizer.train(files=["wiki.train.raw", "wiki.valid.raw", "wiki.test.raw"], trainer=trainer)
分词样例
1
2
3
output = tokenizer.encode("Hello, y'all! How are you 😁 ?")
print(output.tokens)
# ["Hello", ",", "y", "'", "all", "!", "How", "are", "you", "[UNK]", "?"]